Accurate and complete clinical documentation is crucial in today’s rapidly changing healthcare system.
However, given the growing role of technology in our daily lives, it should come as no surprise that healthcare providers now depend on different documentation methods to help manage patients and their health records.
But as with every system, human mistakes are inevitable.
Unfortunately, mistakes in clinical documentation can have significant implications, not just for the patient but also for the organization involved.
This article will discuss common clinical documentation mistakes and how to avoid them in your practice.
Why Do You Need Accurate Clinical Documentation?
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that about 50% of all clinical documentation mistakes are due to administrative mistakes such as incorrect patient records, prescriptions, and identification.
Here are some reasons why patient clinical information must be recorded accurately:
- It enables you to provide optimal patient care.
- It facilitates communication about patient treatment and management strategies among your team members.
- It helps speed up payments and reduces any stress associated with processing claims.
- It reduces the risk of liability in the case of a lawsuit.
Consequences of Clinical Documentation Mistakes
Errors in clinical documentation are expensive. Beyond the financial implications, it could also compromise patient care. The United States healthcare industry loses revenue annually due to improper documentation by healthcare providers.
Here are some of the costs that come with clinical documentation mistakes:
Financial Costs
Errors in invoicing and coding due to inaccurate or incomplete documentation can lead to claims being denied or underpaid.
According to a market data report by Gitnux, medical billing mistakes cost the US healthcare industry an estimated $935 million each week. Therefore, doctors and hospitals must take precautions to guarantee precise records.
Incomplete documentation also makes it harder to keep tabs on patient bills. Because of this, effective payment collection and management of accounts receivable can be difficult.
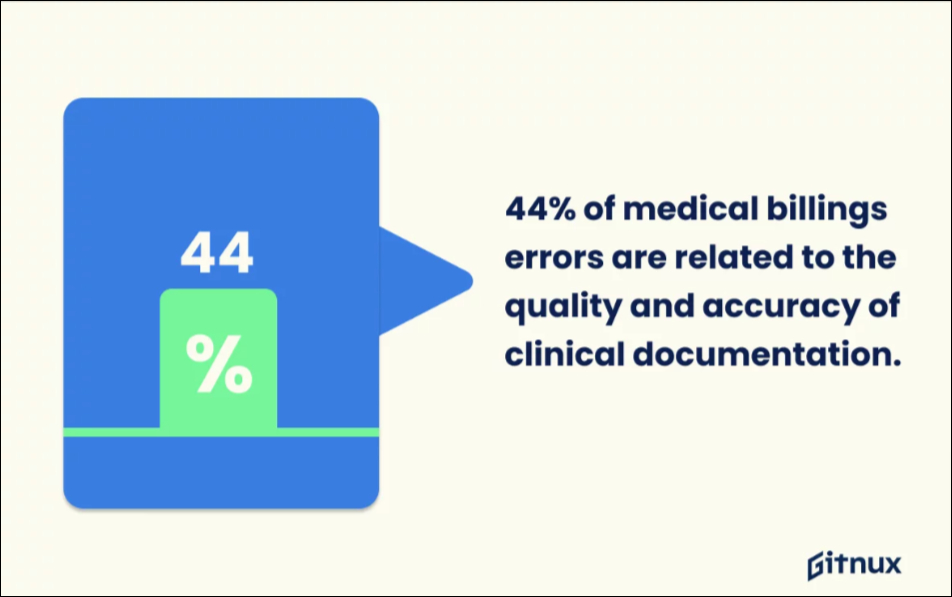
Similarly, poor or inaccurate clinical documentation accounts for 44% of all medical billing mistakes, according to the market data report by Gitnux.
Legal Costs
Malpractice lawsuits can be expensive, highlighting the importance of thorough documentation.
According to a study by CRICO Strategies, 30% of malpractice claims during a five-year period were due to problems with communication, which often involve documentation mistakes.
Sadly, over 1,744 deaths could be linked to these mistakes. Furthermore, legal repercussions, like allegations of malpractice and regulatory fines, may result from inaccurate documentation.
Issues with Quality of Care
Poor documentation can lead to misunderstandings among healthcare providers. More than 25% of medical billing mistakes occur due to typos in clinical documentation, according to Gitnux market data.
Miscommunications of patients’ ailments due to conflicting or unclear information or typographical errors could negatively affect the quality of care and finances.
Reimbursement Issues
Billing and reimbursement issues may result from documentation mistakes, causing a loss of revenue for healthcare organizations.
According to Gitnux, 63% of medical billing errors in the United States result from hospital coding mistakes.

In addition, claim denials, payment delays, and compliance-related fines can all result from insufficient documentation.
Types of Clinical Documentation Mistakes
Errors in clinical documentation can have serious consequences for the patient and may even compromise their safety.
But what kinds of documentation errors might impact the quality of medical care? Here are a few to look out for:
1. Incomplete Documentation
Incomplete documentation is a common source of mistakes in the clinical setting.
Unfortunately, incomplete documentation could lead to life-threatening medical or surgical errors and disruptions in treatment progress.
According to a study assessing the risk and consequences of clinical miscoding due to inadequate documentation, incorrect coding and billing due to incomplete documentation harm healthcare companies’ revenue.
2. Copy and Paste Mistakes
Electronic medical records (EMRs) are convenient, no doubt. They make medical documentation easier and safer. Like every other software, it allows you to copy and paste documents easily.
However, the quality of care can suffer if doctors and nurses copy and paste clinical notes from one patient visit to the next.
Although copy-pasting may save doctors time, it creates more opportunities for mistakes in the documentation. In a recent study by Alexander Muacevic and John Adler, 36% of documentation errors were due to copy-pasting.
Copying and pasting can promote the dissemination of wrong or out-of-date information, produce conflicting notes, and cause extensive notes to obscure crucial clinical information.
3. Misplaced or Conflicting Documentation
Misplaced documentation is still a challenge that plagues health information management. Whether due to data being entered into the wrong field in an EMR or having to scramble for missing parts in a hybrid health-record setting.
If procedure notes, for instance, sometimes wind up in the progress note section, it can confuse other team members.
This conflicting documentation can limit communication among healthcare personnel, leading to mistakes and impaired patient care.
4. Typographic Mistakes

Medication documentation mistakes, especially typos, can significantly impact patient safety.
Medication Administration Record (MAR) charts and other documentation systems are prone to human error when medical personnel input medication names, doses, and other vital information.
For example, deleting or inserting a decimal point is a typical typographical error that can lead to serious dosage mistakes. Let me explain.
If a patient receives ten times the intended amount of a prescription because a decimal point was left out of the documentation, this can have serious consequences.
However, if an extra decimal point is included, the patient could wind up with a dose just a tenth as strong as intended.
5. Unusual Abbreviations
Abbreviations are a major concern across paper and electronic healthcare documentation, even though they can simplify processes.
However, the incorrect use of abbreviations can significantly affect patient care and intervention outcomes, as it can cause misinterpretations and mistakes.
For instance, if a drug is prescribed with the acronym “q.i.d.,” it should be taken four times a day, whereas the abbreviation “q.1.d.” indicates that it should be taken only once daily. Such a mix-up might lead to inappropriate medicine dosages and harmful drug responses.
How to Avoid Common Mistakes in Clinical Documentation

Maintaining accurate healthcare documentation can be challenging. With any system, mistakes are inevitable.
However, with recent advances in technology, it is possible to have your clinical notes written without making mistakes that could be costly. Here are a few ways you can avoid mistakes in your documentation:
Make Your Documentation Clear, Concise, and Consistent

Writing clear and concise notes will make your notes useful to everyone who needs to read them. Be as specific as possible. It would be best if you didn’t use anything nobody else would understand, like obscure acronyms or jargon.
In a study, “Frequency and Types of Patient-Reported Errors in Electronic Health Records,” about one-fifth of patients had mistakes in their medical documentation, and 40% of those people thought it was a major problem.
Maintain uniformity in all patient documentation and be consistent. That is to say, don’t change your methods to suit a variety of patients. All patients need the same degree of detailed documentation.
Use an Electronic Medical Record (EMR)

The likelihood of making a mistake increases when taking clinical notes manually. Reading your notes might be challenging for others, especially if your handwriting needs to be more legible.
Even when you type them on your personal computer, there is still a risk of breaching patient privacy rights.
The problem of illegible handwriting is easily solved by switching to an electronic medical record (EMR) system built to comply with security requirements and boost productivity.
Use PhraseExpander: A Text Expander Tool

A text expander is a computer application that helps you avoid having to type the same thing over and over again. It is not copying and pasting.
It utilizes shortcuts and abbreviations to quickly enter large chunks of information and commonly used phrases and sentences.
PhraseExpander is a tool that fits this description. Designed with physicians in mind, it helps reduce time spent on clinical documentation without sacrificing quality.
Using PhraseExpander means you can write error-free clinical notes and avoid the mistakes of copying and pasting medical documents without sitting hours behind a computer.
The advantages of using PhraseExpander for your clinical documentation are enormous, but here are a few of them:
Autocomplete Feature
PhraseExpander has an autocomplete function that works in any software, reducing the time you spend typing and increasing productivity.
The SmartComplete feature also organizes acronyms into groups, making it easier to locate what you need.
In-built and Customizable Templates
PhraseExpander features pre-defined templates, primarily designed for doctors with a glossary of medical terminologies. Furthermore, you can develop templates to adapt them to your specific needs.
Built For Teamwork

With PhraseExpander, your team members can use text expansion software to complete their documentation faster and with less stress.
PhraseExpander allows you and your team to create individual glossaries or use a shared folder that the whole team can easily access. The teamwork feature promotes consistency in documenting clinical notes.
Get Started with PhraseExpander
Want to learn what PhraseExpander can do for you? Start your free trial
Adopt Documentation Best Practices
In addition to the methods mentioned above, knowing the world’s best practices for clinical documentation is important and highly recommended.
What methods are clinicians worldwide adopting to avoid mistakes in their documentation? Some other ways to avoid mistakes in clinical documentation include:
- Develop techniques for making corrections.
- Practice real-time documentation
- Adhere to the documentation requirements set by relevant regulatory bodies.
- Train your team on efficient documentation practices.
- Manage your time well while documenting.
Conclusion
Healthcare clinicians and administrators all need to work together to reduce the incidence of frequent errors in clinical documentation.
By prioritizing thorough, unambiguous, and consistent documentation methods, doctors can reduce potential errors, improving patient safety and the quality of care.
Furthermore, using technology like text expanders that integrate seamlessly with your EMR for clinical documentation will eliminate common mistakes while documenting. You can find the features mentioned above and many more with PhraseExpander.
